Perception and Sensation
What are the stages of the "perceptual process"?
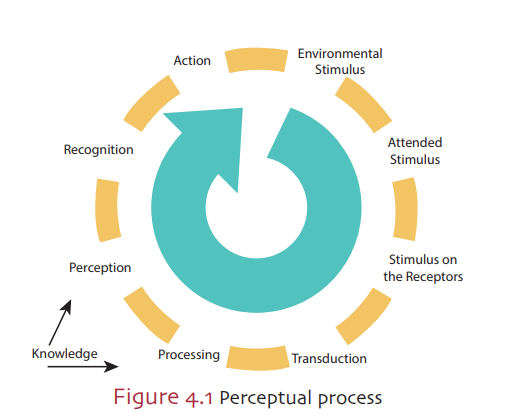
Where does stimulus exist in our life?
Stimulus exists both in the environment and within our bodies. Stimulus in the environment has two aspects: environmental stimulus and attended stimulus
What is "recognition"?
Perception occurs when the electric signals of the leaf-shaped bug representation reach the brain in a transformed form. Realization of the leaf-shaped bug (not leaf) is called recognition;
What is the trichromatic theory based on?
The trichromatic theory is based on the idea that the light of a particular wavelength stimulates the three different receptor mechanisms, each with different spectral sensitivities (also called Young – Helmholtz theory of color vision). These three colors are red, green, and blue. Each of these color-sensitive cone cells has different degrees of sensitivity, with blue cones being the most sensitive and red cones being the least. This activity pattern results in the perception of color.
What is the main principle of the opponent-process theory of color vision?
According to the opponent- process theory of color vision. According to this theory, color perception depends on the reception of pairs of antagonist colors. If we look at a colored pattern and then look away from it, the after-image will have the color “opposite color” of the object we were looking at.
What are the roles of distance cues in the perception of depth?
Distance perception is the act of knowing or recognizing a distance from previous experiences or recollective thought. Depth and distance perception refers to the ability to recognize objects by positioning them in variable distances in the three-dimensional world. Perception of depth is perceived by the distance cues: binocular cues and monocular cues. Binocular cues aid in-depth perception and monocular cues provide the information necessary to feel the depth and the distance in a picture on a two-dimensional paper. However, distance perception doesn’t depend only on optical information like monocular and binocular depth cues. Have you ever gone camping with your friends? Imagine that you are walking through the camping site. You think that the camping site is pretty close to you. What would change the distance between you and the camping site or rather, what would change your distance perception?
What is the law of similarity?
Perceptual organization involves the grouping of elements in an image to create larger objects. In the early 1900s, a group of psychologists called themselves Gestalt psychologists. They proposed the idea that the whole differs from the sum of its parts. Gestalt psychologists argue that if the relationships between the objects around us are uncertain, the simplest and the most consistent arrangements are made to provide a perceptual organization. One of the important perceptual organization laws is the law of similarity, which states that similar things appear to be grouped together
What does the place theory suggest for pitch perception?
The pitch is important because it plays an important role in distinguishing people’s voices and their emotions during the speech. There are several theories that are related to pitch perception: place theory and temporal theory. The place theory suggests that sounds with different pitch generate neural messages in different sets of neurons, which in turn induce different fibers in the hearing cortex. The place theory of pitch perception states that different portions of the basilar membrane are sensitive to sounds of different frequencies. So this theory cannot completely explain how we perceive low pitch sounds that create a synchronised reaction in the basilar membrane
What are the function of monaural and binaural cues in hearing?
Like the monocular and binocular cues that provide information about depth, the auditory system uses both monaural (one-eared) and binaural (two-eared) cues to localize sound. Each ear interacts with the incoming sound waves differently depending on the sound source. For example, the sound from the left side reaches the left ear right before it reaches the right ear. The source of the voice is determined by comparing the time of arrival between the two ears and the intensity of the voice. When the voice is in a low pitch, the time to reach the ear provides more meaningful information. However, when the voice has a high pitch, the intensity provides more valid and meaningful information.
What is macrosmatic?
The sense of smell is important for most species because it is often the primary source of perceiving the environment3. The animals, which have a highly developed sense of smell are macrosmatic.
What is anosmia?
Losing the ability to smell is called anosmia. People who suffer from anosmia show us the importance of smell since these people also lose their ability to taste many foods. The reason for that is the close connection between smell and flavor.
What is Olfactory adaptation?
Olfaction is more important for our survival than we think. It serves as an olfactory warning system in dangerous situations, such as gas leakage or rotten food. Olfactory adaptation is the reduction in response to a continuing smell.
What is the difference between "Taste Perception" and "olfaction"?
We mentioned olfaction as a sense that detects molecules entering the nose in gaseous form. Now we move on to taste, which detects molecules that enter the mouth in solid or liquid form. In general, the taste sensation has the following categories: sweetness, sourness, saltiness, and bitterness.
What does the gate-control theory of pain claim?
Although researchers cannot completely explain the pain, they can explain the process of injury and brain’s role. In the 1960s, Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall proposed a theory about the pain that is called the gate-control theory of pain7. According to this theory, pain signals travel from the body to the brain through a gate in the spinal cord. Gate refers to the pattern of neural activity which functions as a gate. This activity either stops pain signals or allows them to pass. Openness or closeness of the gate is determined by the signals of the brain. For example, when you focus on your pain, you feel more pain; but if you ignore it you can experience a decrease in your pain perception. Also, other signals from the skin senses, like ice or heat, can close the gate
What does the law of closure claim?
According to the law of closure, our brains sometimes fill in gaps in order to create a meaningful image
What are the principles of the law of proximity?
There are four principles of the law of proximity that the Gestalt psychologists proposed to explain how perceptual grouping occurs: Grouping by (a) proximity; (b) common
region; (c) connectedness and (d) synchrony.
What does the proximity principle of the law of proximity claim?
It claims that When things are near each other, they appear to be grouped together.
What does the principle of common region claim?
Elements that are within the same region of space appear to be grouped together, and this phenomenon is called principle of common region
What does the principle of uniform claim?
The principle of uniform connectedness states that a connected region of visual properties, such as lightness, color, texture, or motion, is perceived as a single unit.
What does the principle of synchrony claim?
The principle of synchrony states that visual events occurring at the same time are perceived as belonging together.